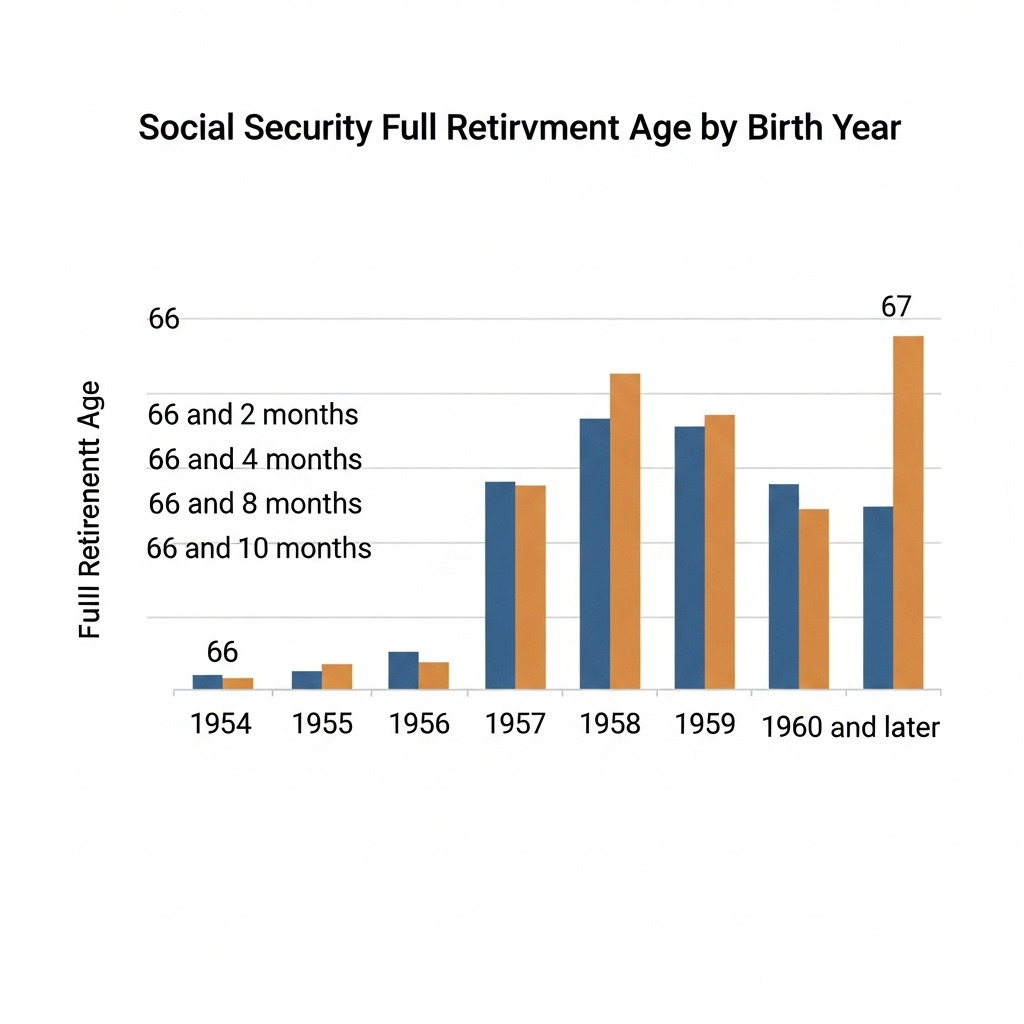
As Americans plan for their financial futures, questions surrounding the USA retirement age increase are common. While no new legislation was passed in 2025 to alter the retirement age, the final phase of a decades-old, scheduled increase is now taking full effect, permanently setting the nation’s full retirement age for Social Security benefits at 67 for everyone born in 1960 or later.

USA Retirement Age Increase in 2025
To clarify the current rules, here are the essential facts about the Social Security retirement age as of 2025.
| Key Fact | Detail & Significance |
| Full Retirement Age (FRA) | The FRA is now 67 for anyone born in 1960 or later. This is the age at which you are eligible to receive 100% of your earned Social Security benefits. Social Security Administration |
| Reason for the Change | The increase is the final step of a gradual change enacted by the 1983 Social Security Amendments, designed to improve the program’s long-term financial stability. |
| Early Retirement Eligibility | Americans can still begin receiving Social Security benefits as early as age 62, but the monthly payment will be permanently reduced. |
| Impact on Benefits | Claiming at 62 now results in a 30% reduction in monthly benefits for those with an FRA of 67, compared to waiting until full retirement age. |
The Scheduled Rise to a Full Retirement Age of 67
The ongoing adjustment to the U.S. retirement age is not a recent development but the result of bipartisan legislation signed into law by President Ronald Reagan more than four decades ago. The 1983 Social Security Amendments were passed to address projected shortfalls in the system’s funding, primarily driven by increasing life expectancies and changing demographic trends.
The law established a gradual increase in the full retirement age (FRA), the age at which a person can claim their full, unreduced retirement benefits. For decades, the FRA was 65. The 1983 law implemented a schedule to slowly raise it to 67.
“This phased-in approach was designed to give Americans time to plan and adjust their retirement strategies,” said Dr. Alicia Munnell, director of the Center for Retirement Research at Boston College, in a recent analysis. “The final step of that plan is now concluding as the age 67 FRA becomes the standard for all future retirees.”
Who Is Affected by the Current Changes?
The increase directly impacts individuals born in 1960 and later. For this group, the full retirement age is now firmly set at 67. Those born between 1955 and 1959 had a sliding-scale FRA, increasing by two months for each birth year. For example, someone born in 1959 has an FRA of 66 years and 10 months.
How This Impacts Your Social Security Benefits
Understanding the revised eligibility rules is crucial for retirement planning. While you can still claim benefits at 62, the financial consequences of doing so are now greater.
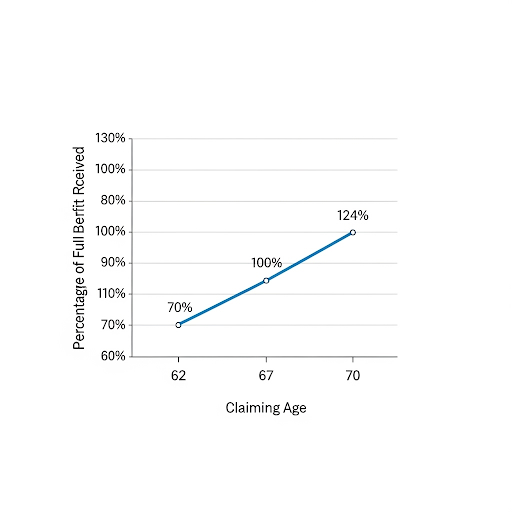
- Claiming at Full Retirement Age (67): If you were born in 1960 or later and wait until you turn 67, you will receive 100% of your primary insurance amount (PIA), which is the benefit calculated from your lifetime earnings.
- Claiming Early (at 62): If you choose to claim benefits at the earliest possible age of 62, your monthly payments will be permanently reduced by 30%. This reduction is calculated to balance out the longer period over which you will receive payments.
- Delaying Benefits (up to 70): For every year you delay claiming benefits past your FRA, you earn delayed retirement credits. These credits increase your monthly benefit by 8% per year. If you wait until age 70, your benefit will be 24% higher than your full retirement amount.
“The decision of when to claim is one of the most significant financial choices a person will make,” states the Social Security Administration (SSA) on its website. The agency provides calculators and resources to help individuals model different scenarios.
Future Debates on Retirement Security
With the 1983 changes now fully implemented, policymakers in Washington continue to debate the long-term future of Social Security. The program’s trustees report annually on its financial health, and projections often indicate future funding challenges that may require legislative action.
According to a recent report from the Congressional Budget Office (CBO), various proposals are periodically discussed to ensure solvency for future generations. These proposals sometimes include further increasing the full retirement age, adjusting the formula for calculating annual cost-of-living adjustments (COLAs), or modifying the tax structure that funds the program. However, it is important to note that these are currently just proposals, and no new laws have been passed.
As of 2025, the retirement age structure is stable and operating under the framework established in 1983. Financial advisors recommend that younger workers plan for a full retirement age of at least 67 and consider the significant benefits of delaying claims if their health and financial situation permit.
7 Million People in UK Just Got Bad News About Their Retirement; Here’s What Happened
FAQs
1. What is the full retirement age for someone turning 65 in 2025?
For an individual born in 1960 who turns 65 in 2025, their full retirement age is 67. They will need to wait two more years to receive their full, unreduced Social Security benefit.
2. Can I still retire and stop working at 62?
Yes, you can stop working at any age. However, you can only begin receiving Social Security retirement benefits at age 62, and these benefits will be permanently reduced if claimed before your full retirement age of 67.
3. Is Congress planning to raise the retirement age again soon?
While various policy proposals to adjust the retirement age are sometimes debated in Congress to address long-term Social Security funding, there is no active legislation with broad support to increase the age further at this time. The current law remains unchanged.






